Update Factory Client for Android Embedded Devices¶
Introduction¶
Update Factory is the OTA software update and delivery platform used by Kynetics based on the Eclipse hawkBit project. In the process to align OS embedded development with the best practices of software development including Building and Delivery pipelines, we have found that it is beneficial for our customers to provide as much automation as possible to quickly test custom Android OS images built for their target devices. For this purpose Update Factory has proven to be a solid and easy to use platform to manage OS image deployments during development and production.
Customers can subscribe to Update Factory as a service, outside the development services offered by Kynetics.
Kynetics provides Update Factory client implementations for both Open Embedded and Android OS.
In particular UF Android Service is Kynetics’ Android implementation of a hawkBit client.
The Update Factory Android client, which implements the DDI APIs of hawkBit, is composed of two modules:
- uf-client-service
- uf-client-ui-example
As part of the standard delivery pipeline for OS images, Kynetics provides also binary images (APKs) of both modules.
Kynetics usually delivers updates and binary packages through the Update Factory platform itself.
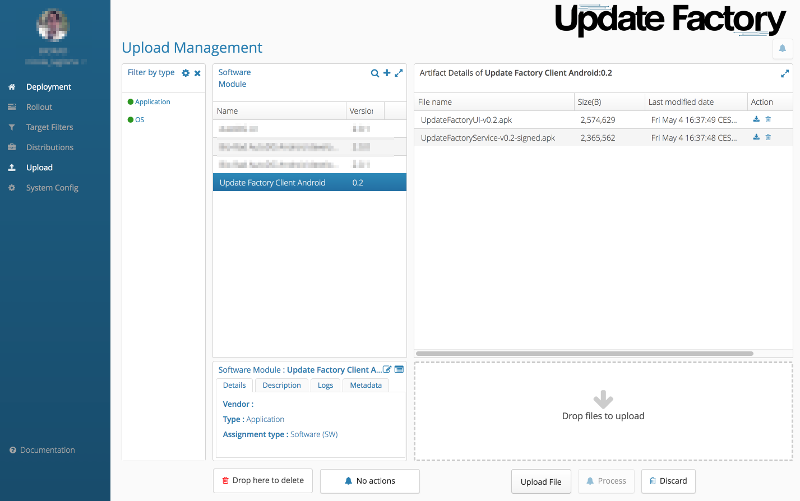
It is possible from the Upload section to download, using the browser, the APKs of both client-service and client-ui.
Usually both packages are included as artifacts in a single software module named Update Factory Client Android.
To download an artifact, simply click on the download icon in the Action column.
Uf-client-service¶
Uf-client-service is an android service that runs in the background and manages the update process. The service implements the DDI APIs; the state machine and status messages.
Uf-client-service must be installed as a SYSTEM application to work correctly. To be a system app it is necessary to sign the application with the platform key which can be the test key provided by default by the Android build system or a custom one created for production purposes. Please refer to this technical note for more information regarding how to sign system applications.
Uf-client-ui-example¶
Uf-client-ui-example is a GUI Android App that communicates with the uf-client-service. Uf-client-ui-example is useful to:
- configure the uf-client-server
- monitor the state of the service
- display the service log
If only the android service is needed for the client-server communication, the client ui is very useful for logging purposes and for having visual feedback of the current state of the update process.
Configuration file¶
When a new customer is registered on Update Factory, Kynetics provides a Tenant_id (customer identification). Every device is identified uniquely by its Controller_Id. Usually it is a best practice to identify a device by its MAC address. A pretty common naming convention for Controller_id is: device-MAC_ADDR.
The uf-client-service can be configured using the UI app or with a with a configuration file.
The service checks if the file has been changed every time the service is started.
If the file is changed then the service uses the new configuration.
The configuration file is called ufConf.conf and must be located on the device PATH:
/sdcard/UpdateFactoryConfiguration/
adb push ufConf.conf /sdcard/UpdateFactoryConfiguration/ufConf.conf
after the service app has been installed successfully with:
adb install -t UpdateFactoryService.apk
and the UI (optional)
adb install -t UpdateFactoryUI.apk
The first time, the service app must be started manually with: on Android 7.1.2 and earlier
adb shell am startservice -a com.kynetics.action.BIND_UF_SERVICE
adb shell am start-foreground-service -a com.kynetics.action.BIND_UF_SERVICE
On Android 9.0, to read the configuration file, the Update Factory service needs the Android STORAGE permission. The user needs to manually grant it from the Android settings, under 'Settings/Apps/Update Factory Service/Permissions'.
This is an example of a complete Update Factory configuration file.
tenant=TEST_TENANT
url=https://personal.updatefactory.io/
controllerId=device-00DE0212A4EE
gatewayToken=
targetToken=
apiMode=true
enable=true
updateFactoryServer=true
The fields: tenant, controllerId and url are mandatory.
The default value for gatewayToken and targetToken is an empty string.
A minimal valid configuration file (if the TEST_TENANT tenant doesn't permit anonymous authentication, then all http requests fail with 401 Unauthorized) is:
tenant=TEST_TENANT
url=https://personal.updatefactory.io/
controllerId=device-00DE0212A4EE
Uf-client-service reset¶
If it is necessary to hard reset the service, just clear application data from Android settings and restart the device
Machine states¶
It is important to understand what the states are of the state-machine implemented in the uf-client-service.
This section is intended to provide a detailed list of all of the states, which shows both detailed and fine grained client-server interaction during the update process. States are displayed by the log view in the client ui app.
- WAITING: the client service is waiting for a command from the server. When the timeout is expired, the client calls the controller base pool resource API to find out if there are new actions. The waiting state can include a suspend state like UPDATE_DOWNLOAD or UPDATE_READY.
- CONFIG_DATA: the client is sending some meta information to the server through the config data API
- UPDATE_INITIALIZATION: a new update is available from the server. The service calls the API to retrieve all artifact links for download.
- UPDATE_DOWNLOAD: the client begins to download the artifacts (like an Android OTA or apk).
- SAVING_FILE: the service is saving the artifact on the embedded device.
- UPDATE_READY: all of the artifacts are downloaded and stored on the embedded device.
- UPDATE_STARTED: the device tries to apply the update (during this state the device is restarted in recovery mode).
- CANCELLATION_CHECK: the device checks if the update server wants to cancel an update (that isn't yet applied).
- CANCELLATION: the device cancels the update and sends a feedback to the server.
- UPDATE_ENDED: the update is completed and the client is sending the update result to the server.
- COMMUNICATION_FAILURE: last communication with the server failed (FAILURE event). When the timeout is expired the client retries to communicate with the server.
- COMMUNICATION_ERROR: server responds with an error message. When the timeout is expired the client tries to re-establish communication with the server.
- AUTHORIZATION_WAITING: the client is waiting for the user authorization to download or apply the update.
- SERVER_FILE_CORRUPTED: the file on the server is corrupted by checking the signature. The client sends feedback to the server.
Events¶
The transition between two states (or when the device stays on the same state) is caused by some kind of event. Events are usually sent to any Android application (like the ui-client-example is registered to the service).
- SLEEP_REQUEST: there isn't any new command from the server. Usually these events are generated when the client stays in the WAITING state indefinitely.
- UPDATE_CONFIG_REQUEST: upon server request, the client provides new configuration data. The client is on the CONFIG_DATA state.
- SUCCESS: generic success events are generated by a state transition.
- FAILURE: the client can't communicate with the server because of an error (typically when the connection doesn't work).
- ERROR: the client receives a response with a status code 4XX or 5XX.
- UPDATE_FOUND: this event is generated when the server provides a link to an artifact. If the artifact is a new update, the client transitions to the UPDATE_INITIALIZATION state.
- DOWNLOAD_REQUEST: artifacts are available on the server for download.
- DOWNLOAD_STARTED: artifact download is started.
- FILE_CORRUPTED: an artifact is downloaded twice with the same hash that is different from the hash of the file on the server.
- CANCEL: this event is raised when the server asks to the client to cancel an update process.
- UPDATE_ERROR: the client can't apply the update because of an error.
- AUTHORIZATION_GRANTED: for soft updates the user has to acknowledge the update. For a forced update, user authorization is not required.
- AUTHORIZATION_DENIED: the user denies the soft update.
- RESUME: a suspend state is resumed.
- DOWNLOAD_PENDING: client is downloading a file.
- FORCE_CANCEL: the update is forced to terminate on the server.
- AUTHORIZATION_WAITING: before starting to download any artifact or apply a soft update, an authorization is pending from the user.